An unshakable ledger for documenting transactions and tracking assets, Blockchain technology builds trust.
Now, what is the real catch about this technology? Let us discuss this in recognition with the database of Wikipedia.
Blockchain enables people to make entries into a data record which the user community has control of its updates and amendments. Similarly, in Wikipedia, no single entity administers the entries.
Moreover, the digital backbone of Wikipedia is almost similar to the centralized and highly protected database which the contemporary financial and government institutions maintain. The update management or the owners hold the authority of centralized databases.
However, the Blockchain technology-crafted distributed database holds an essentially different digital backbone. The users can witness the fresh version when one edits the Wikipedia’s database. But, in a Blockchain’s situation, every network node independently updates the record.
This reflects an upheaval in data distribution and registration which discards the necessity for a trustworthy entity to propagate digital relationships. And it is this difference which defines the fertile functionality of Blockchain technology.
Blockchain isn’t a freshly new technology
It, rather, is a synthesis of proven effective technologies exercised in a totally new way.
Blockchain stems to be a smart coalescence of three technologies that made Nakamoto’s idea relevant and useful. The orchestration of Private Key cryptography, the internet and the incentivization protocol led to the recognition of the Blockchain technology.
Thus, the resultant production is an arrangement for digital interactions that rejects the idea of depending on trustworthy third parties. In addition, the work of armoring digital relationships tends to be unstated and implicit which the technology’s sturdy architecture supplies.
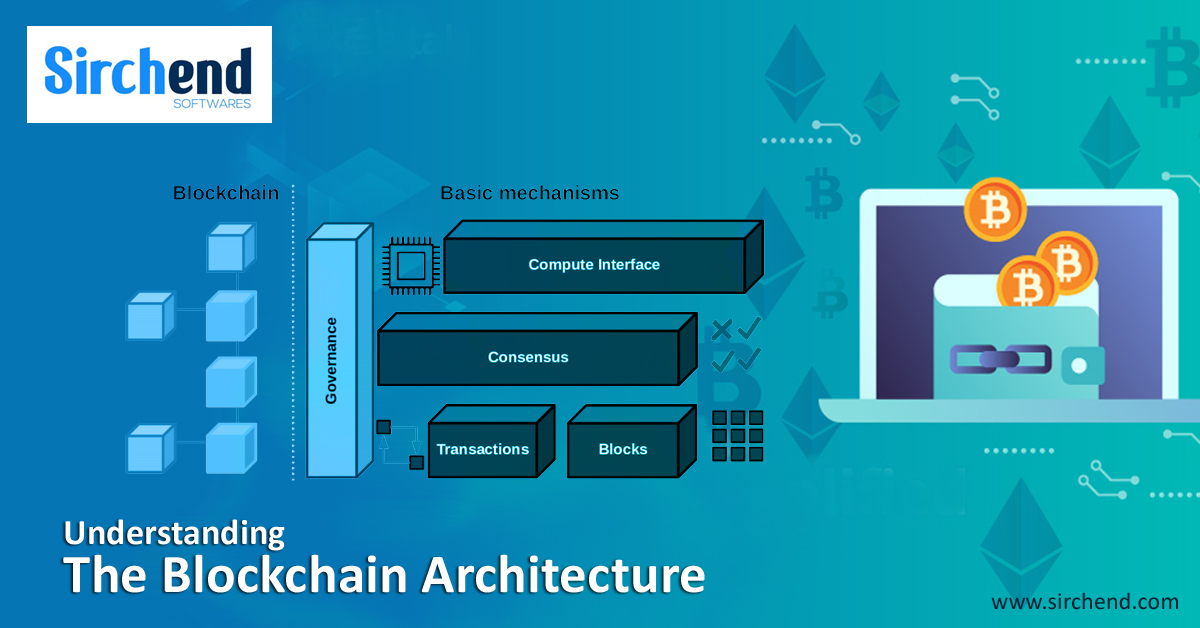
Vital Elements of the Blockchain technology
The three underlying key components make up to define the soul of a blockchain.
Distributed Ledger Technology
The network contenders enjoy access to the distributed ledger along with its irrevocable transaction records. This is, essentially, a shared ledger that records transactions only once discarding the duplication effort which is the trait of conventional business networks.
Apt Contracts
Speed is a guarantee in blockchain technology. And to accelerate transactions, smart contracts, which is a collection of rules, is stashed on the blockchain which then is automatically conducted. It has the potential to comprehend and define scenarios for corporate bond transfers and more.
Unshakable Records
After the process of documentation into the ledger, participants receive hindrances from altering or interacting with the transaction. Now, on the off chance of an error, they must insert a fresh transaction with intentions to reverse the complication. Finally, this makes the both the transactions visible.
How Blockchain Technology actually works
The indulgence of three technologies synthesize together to propagate a new use case namely the blockchain technology. Herein, lies the discussion of how these three coordinate together to armor digital relationships.
Cryptographic keys
Suppose, two individuals transact over the internet. Each holds a public and private key. The component’s central aim is to create a highly secure identity reference. Now, the identity is dependent on the possession of the public and private cryptographic key combination.
Moreover, this combination builds a highly effective and important digital signature. And in return, the digital signature renders a strong authority of ownership.
Identity
The powerful ownership isn’t sufficient for securing the relationship. Now, authorization should be coupled with a vehicle of approving permissions and transactions. However, this starts with a distributed network in case of Blockchain technology.
A Distributed Network
Bitcoin blockchain is an enormous network wherein validators state an agreement that they noticed a particular event take place at the same time as others did. Not to mention, mathematical verification validates such event.
Now, this indicates that in order to secure a network, the size of it is extremely necessary. Bitcoin, at the time of writing, secures 10,000 banks across the globe and 3,500,000 TH/s.
A System of Record
An extremely useful mode of digital interaction emancipates when the cryptographic keys orchestrate with the network. The method initiates with one of them taking their private key, addressing an update or announcement regarding your intent of sending an amount of cryptocurrency and sticking it to the receiver’s key.
Protocol
There is a block which contains the digital signature, relevant data, the timestamp and the keys on the five sides. And this is broadcasts to each and every node of the network.
Network overhauling protocol
The mission of the protocol, with Bitcoin, is to disregard the possibility of the same Bitcoin to be used in a separate transaction. And this takes place in such a manner that makes it challenging to identify. Therefore, this is how Bitcoin aims to act as gold.
So, Bitcoins along with their base units namely satoshis should be distinct and unique to hold value and be possessed. In order to obtain it, the nodes maintain a history of transactions for each cryptocurrency by functioning to resolve the evidence-of-work.
Moreover, they tend to vote with the CPU power unravelling their opinion about the fresh blocks or discarding invalid blocks.
Ethereum Blockchain
Essentially formulated as the ultra-transparent ledger arrangement for enabling Bitcoin to perform on, the Blockchain technology secures financial and bureaucratic institutions with their absolution aspect.
In 2013, the Vitalik Buterin, a developer, published a white paper which made a proposition for a platform combining the conventional functionality of blockchain with one principle difference. That is, the conduction of computer code. And it is then that the Ethereum Project was born.
Furthermore, Ethereum blockchain enables developers to craft and build sophisticated programs which can invite interaction between each of them on the blockchain.
Tokens
Ethereum developers build tokens in order to showcase digital assets. Also, the purpose of them is to find the ownership as well as contrive its functionality respecting a set of development instructions.
Now, tokens can be concert tickets, music files or even an ailing person’s medical records. This widens the prowess of blockchain technology to infiltrate industries like government sectors, media and identity security.
In addition, plenty of companies are currently programming and developing ecosystems that would run on this advancement. Such a groundbreaking automation can combine with another powerful innovation: IoT solutions to transform the world entirely. In this way, stealthily, such developments are recasting the world.
Furthermore, in this way, Blockchain technology is currently giving tough challenges to the current status quo of the technological revolution.